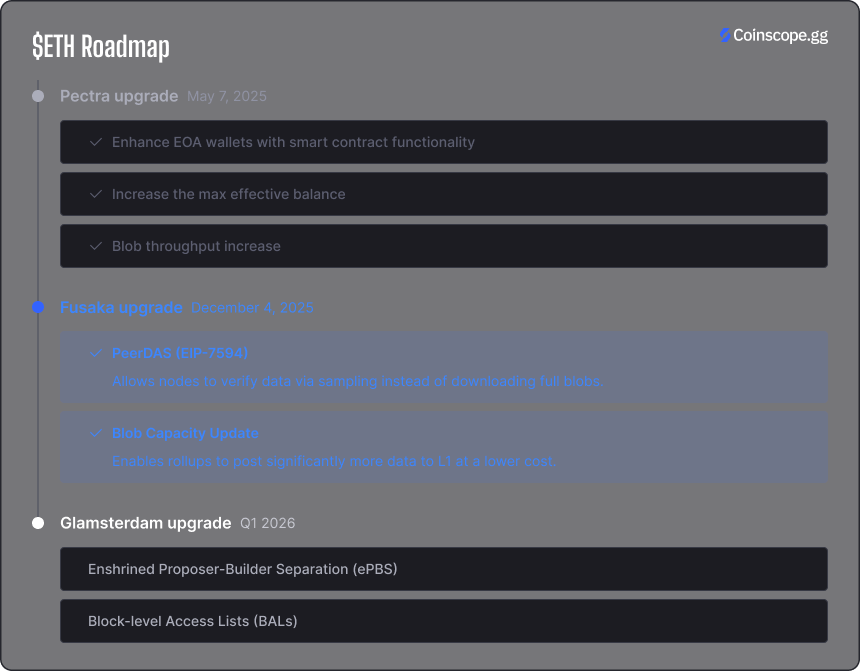
The Ethereum Fusaka upgrade was officially activated on mainnet on December 3, 2025. This hard fork delivered a critical patch that optimizes L2 fees and data availability within Ethereum’s rollup-centric architecture.
There are two main technical breakthroughs:
- PeerDAS (EIP-7594): Allows nodes to verify data via sampling instead of downloading full blobs.
- Blob Capacity Update: Enables rollups to post significantly more data to L1 at a lower cost.
According to core devs, Fusaka, combined with the upcoming BPO (Blob Parameter Only) forks, is projected to cut L2 data fees by an additional 40–60%.
From an L2 perspective, the expected impacts are:
- Lower Onboarding Costs: Reduced fees for CEX→L2 deposits and standard bridges.
- Cheaper Trading: Higher batch efficiency creates room to minimize gas costs for DEXs and derivatives.
- Scalable Social/Gaming Apps: Lowers the barrier for high-frequency, low-value transactions. Efficient Airdrops: Drastically reduces the cost of large-scale claims and point campaigns.
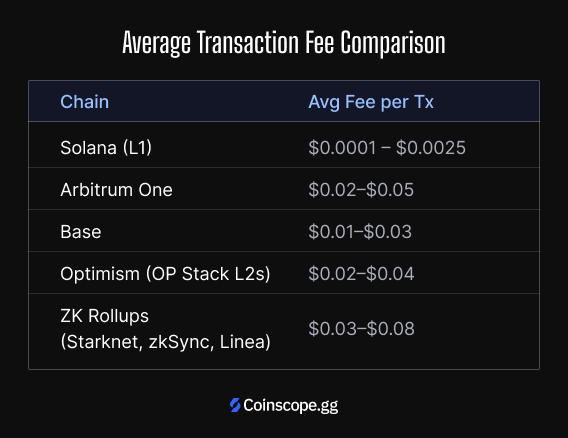
Following the previous Dencun upgrade(March 13, 2024), many rollups saw data costs drop by up to 10-100x. Fusaka is widely viewed as the "accelerator" that cements this trend, pushing average fees comfortably into the sub-cent range ($0.005–0.01).

Historically, high-throughput Alt-L1s like Solana have offered meaningfully lower fees than Ethereum-based rollups. Solana’s average fees are typically quoted in the $0.0001–0.0025 per tx range, while major Ethereum L2s, after Dencun, have moved from tens of cents (≈$0.20) down toward roughly a few cents per tx (≈$0.02–0.05) on many rollups.
What's Next?
The focus now shifts to the Glamsterdam upgrade, currently targeted for H1 2026. Discussions for Glamsterdam center on protocol-level improvements like ePBS (in-protocol Proposer-Builder Separation) and Block Access Lists, aimed at refining block production and MEV handling.
Key Ethereum upgrades and rollup milestones will continue to be tracked on @coinscopegg